I2C Bridge and Node with Arduino sketch¶
- class page Networking and Communications
-
hello.I2C.45.bridge board
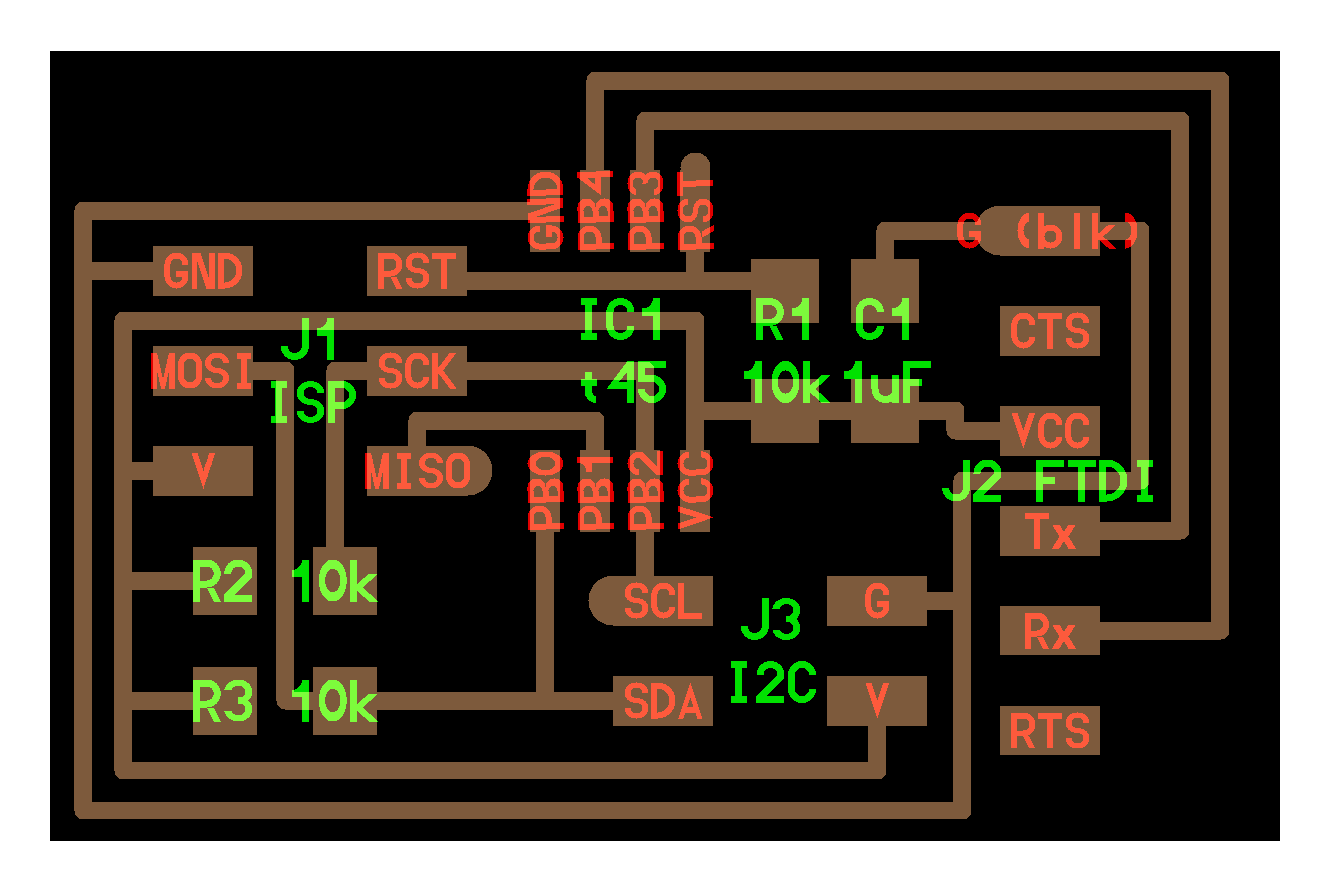
-
hello.I2C.45.node board
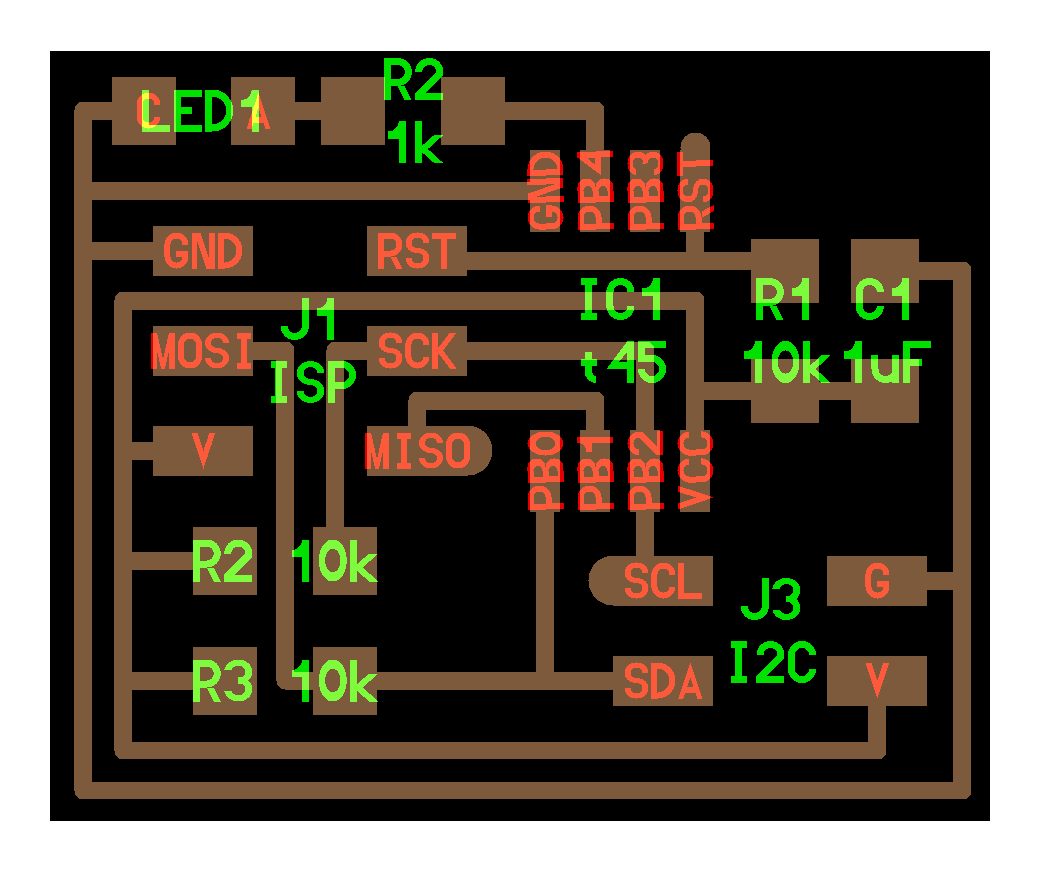
Install ATTinyCore¶
ref.Arduino IDE に ATtiny45/85/2313 他の開発環境を組み込む
Arduino IDE > preference > board manager URL > http://drazzy.com/package_drazzy.com_index.json
 Tool > Board > Board Maganer > Serch: attiny > Select:ATTInyCore by Spence Konde > Install
Tool > Board > Board Maganer > Serch: attiny > Select:ATTInyCore by Spence Konde > Install
 Tool > Board:> ATtiny Universal > ATiny24/44/84
Tool > Board:> ATtiny Universal > ATiny24/44/84

Note
ATTinyCore can use
TEST 1: SoftwareSerialExample¶
Arduino > File > Sketch Example > ATTiny25/45/85 Sketch Example > SoftwareSerial > SoftwareSerialExample This sketch can be used in Arduino Uno and Attiny45 I2C Bridge board.
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(3, 4); // RX, TX
void setup()
{
// Open serial communications and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(57600);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for Leonardo only
}
Serial.println("Goodnight moon!");
// set the data rate for the SoftwareSerial port
mySerial.begin(4800);
mySerial.println("Hello, world?");
}
void loop() // run over and over
{
if (mySerial.available())
Serial.write(mySerial.read());
if (Serial.available())
mySerial.write(Serial.read());
}
TEST 2: Simplify SoftwareSerial for ATtiny45¶
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(3, 4); // RX, TX
void setup() {
mySerial.begin(4800);
mySerial.println("SoftwareSerial_Hello");
}
void loop() {
if(mySerial.available()){
mySerial.write(mySerial.read()); // 1 -> 1
// mySerial.println(mySerial.read()); // 1 -> 49 //文字列の最後に改行コードであるCR(\r)とLF(\n)を付与して送信
char c = mySerial.read();
// mySerial.write(c); // 1 -> 1
// mySerial.println(c); // 1 -> 1
// mySerial.print(c); // 1 -> 1
}
}




TEST 3: I2C Master¶
For Arduino Uno
ATtiny45 has 4kB(4096B) Flash. This sketch is 4516B(110%).
ATtiny85 has 8kB Flash. It can be used.
#include <Wire.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(3, 4); // RX, TX
void setup() {
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
}
mySerial.begin(4800);
mySerial.println("SoftwareSerial_Hello");
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus (address optional for master)
}
void loop() {
Wire.requestFrom(8, 6); // request 6 bytes from slave device #8
//while (Wire.available()) { // slave may send less than requested
char c = Wire.read(); // receive a byte as character
mySerial.print(c); // print the character
//}
delay(500);
}
I2C Slave¶
#include <Wire.h>
void setup() {
Wire.begin(8); // join i2c bus with address #8
Wire.onRequest(requestEvent); // register event
pinMode(PB4, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
delay(100);
}
// function that executes whenever data is requested by master
// this function is registered as an event, see setup()
void requestEvent() {
digitalWrite(PB4, HIGH);
delay(8000);
Wire.write("hello "); // respond with message of 6 bytes
// as expected by master
digitalWrite(PB4, LOW);
delay(8000);
}
Burn fuses from Terminal without makefile¶
ref.AVR Fuse Calculator
ref.fuse bits - FabISP
CKDIV8 programmed(0)
$ avrdude -p t45 -P usb -c atmelice_isp -U lfuse:w:0x62:m
CKDIV8 unprogrammed(1) -> don’t divide
$ avrdude -p t45 -P usb -c atmelice_isp -U lfuse:w:0xE2:m